oxygen delivery devices and flow rates australia
Of the commonly available devices promoted for O 2 delivery to injured divers similar P tc O 2 and nasopharyngeal F I O 2 values were obtained with the three devices tested. This oxygen delivery devices and flow rates chart shows the o 2 delivered measured for each tool.
This delivers to the patient a flow rate of 45 liters per minute and an oxygen concentration of 35 percent.
. 4060 FiO2 at a flow of ³5 Lmin Delivery of higher FiO2 levels than nasal cannulae. A simulated patient and oxygen sensor were used to compare wafted oxygen concentrations for six delivery devices in various positions and oxygen flow rates. Variable devices are affected whereas fixed are theoretically not.
Comfort cost easy titration. Non-rebreather reservoir mask 60 FiO2 at a flow of 15 Lmin. Room air is 21 O2 and air from the walloxygen delivery device is 100 O2.
Same as Salter with added benefit of providing higher flow rate and consistent FiO2 for patients with high oxygen. The paediatric non-rebreather held below the face produced. It can be set to deliver between 10 and 15 Lmin 1 8095 oxygen.
The required oxygen flow rate can be very low often between 08 and 15 Lmin-1. MORS with an oronasal or intraoral mask demand valve with an intraoral mask and NRB at a flow rate of 15 Lmin-1PtcO2 and nasopharyngeal F I O 2 values were. Delivery of higher FiO2 than simple mask.
For example the recommended flow rate for a 35 of venturi valve is 8 liters per minute. Increasing the flow rate delivered through a nasal cannula increases the delivered oxygen concentration by 2-4 per liter per minute increase. A one-way valve between the mask and the reservoir bag prevents the patient from inhaling expired air.
Delivered O2 Concentration. 24-45 at 1-6LPM respectively in adults. Only oxygen tubing and the paediatric non-rebreather mask consistently delivered wafted oxygen concentrations above 30.
The recommended initial oxygen flow rate for open-circuit systems employing a non-rebreather mask has long been 15 Lmin-1. MORS with an oronasal or intraoral mask demand valve with an intraoral mask and NRB at a flow rate of 15 Lmin¹. Different oxygen flow rates result in a highly variable and unpredictable FiO 2 Rebreathing of CO 2 can occur with O 2 flow rates of less than 2 L O 2 lmin or if minute ventilation is very high 4 Lmin of oxygen flow delivers an FiO 2 of about 03504 providing there is.
A paediatric simple Hudson face mask PFM Oxygen Mask Child Aerflo Australia a paediatric non-rebreather mask PNRB. If the nasal prongs are curved these should face posteriorly to the patient. This reduces the overall oxygen needed during rest and with exerciseThis table helps doctors choose theTypical fio.
Consumption is the liters per minute set by the user. Of the commonly available devices promoted for O₂ delivery to injured divers similar PtcO₂ and nasopharyngeal F I O₂ values were obtained with the three devices tested. Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature.
FIO2 depends on the patients pattern of breathing. Oxygen delivery devices generally fall into two categories - variable and fixed - indicating how they are affected by the patients flow rate MV. 1 shows the simulated patient oxygen sensor and device positioning apparatus.
The increased efficiency is achieved through increased complexity. Set flow rate at 1 to 4 litres per minute. 2435 FiO2 at a flow of 14 Lmin.
Oxygen delivery devices positioning and flow rates Six different oxygen delivery devices were investigated. Oxygen flow. Looping the tubing around the patients ears and bring it to the front of the patients chest.
The HFNC is an oxygen-delivery system that includes an airoxygen blender humidifier heater and nasal cannula to deliver precise and very high flow oxygen to your patient. Apply the nasal cannula to the patients nose first. Increasing the flow rate to 10 liters per minute increases the total flow to the patient but the oxygen concentration delivered remains at 35.
Connect the face mask to the oxygen cylinder.

Preoxygenation Deoxygenation And Reoxygenation During Intubation

Estimated Inspired Oxygen Concentration Download Table
Automatic Oxygen Titration Versus Constant Oxygen Flow Rates During Walking In Copd A Randomised Controlled Double Blind Crossover Trial Thorax
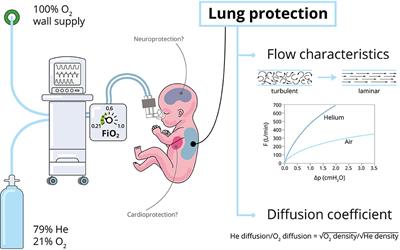
Frontiers Neonatal Applications Of Heliox A Practical Review
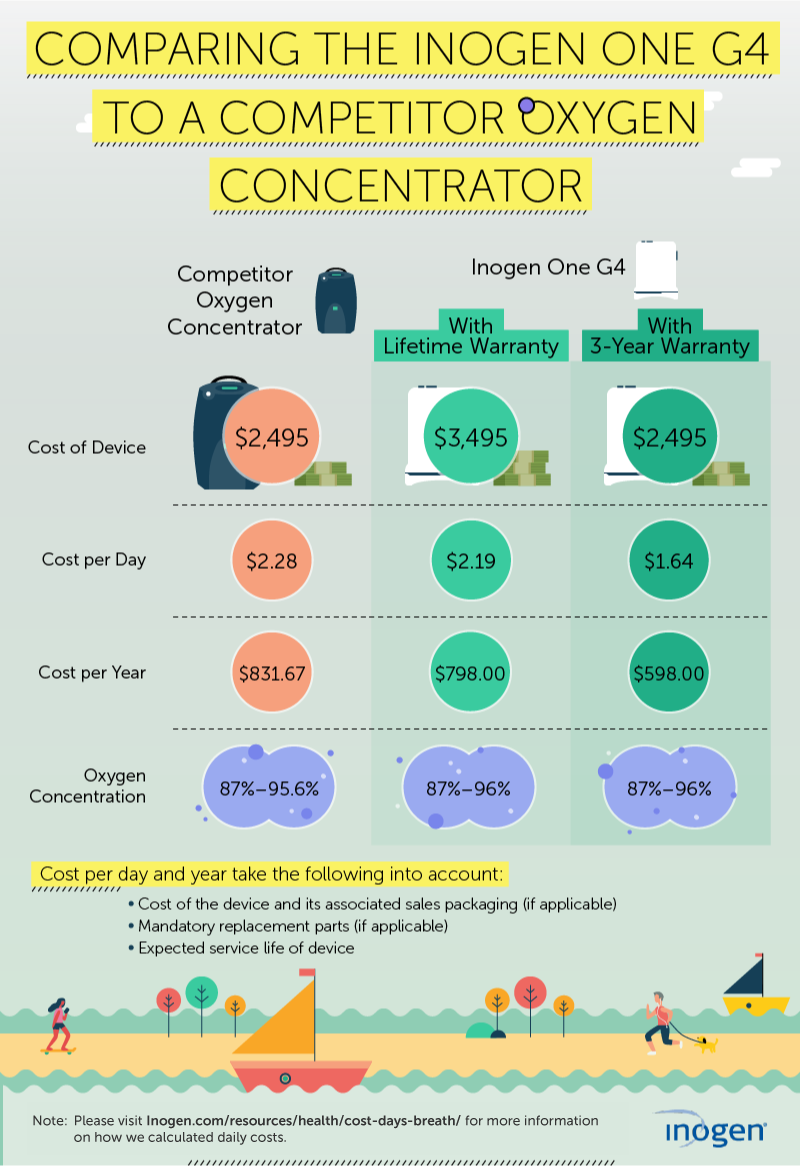
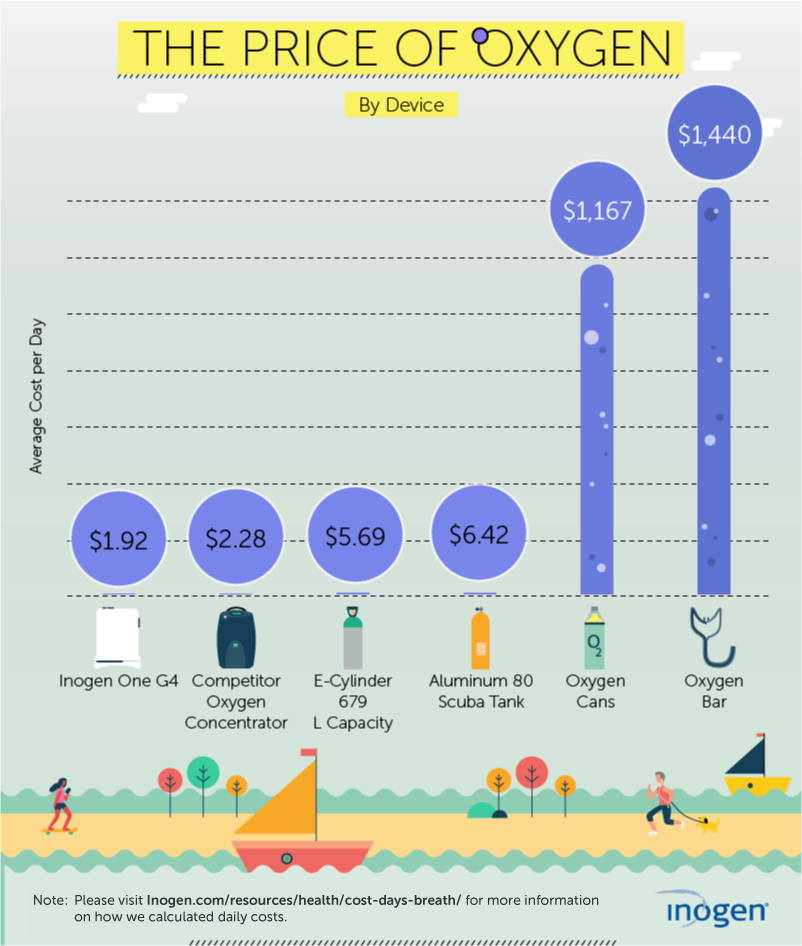
Cost Of Oxygen Portable Oxygen Concentrator Cost Inogen

Cost Of Oxygen Portable Oxygen Concentrator Cost Inogen

Oxygen Delivery System Side 1 Nursing School Notes Nursing Notes Respiratory Therapist Student

O Two Single Use Cpap Otwo Com

Thoracic Society Of Australia And New Zealand Position Statement On Acute Oxygen Use In Adults Swimming Between The Flags Barnett 2022 Respirology Wiley Online Library
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery
German S3 Guideline Oxygen Therapy In The Acute Care Of Adult Patients Fulltext Respiration 2022 Vol 101 No 2 Karger Publishers

Liberal Or Conservative Oxygen Therapy For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Nejm

Thoracic Society Of Australia And New Zealand Position Statement On Acute Oxygen Use In Adults Swimming Between The Flags Barnett 2022 Respirology Wiley Online Library

High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy In Patients After Cardiac Surgery Semantic Scholar

Automatic Oxygen Titration Versus Constant Oxygen Flow Rates During Walking In Copd A Randomised Controlled Double Blind Crossover Trial Thorax
